Each fiber has particular properties which help us to decide which particular fiber should be used to suit a particular requirement. Certain fiber properties increase its value and desirability in its intended end-use but are not necessary properties essential to make a fiber.
Fiber Properties for specific requirements
The utility of fibers is broadly categorized into 2 different uses- one is Apparel or Domestic use and the other is Industrial use. In order to be used in each of these categories, the fiber has to meet some specific requirements. They are:
Apparel/Domestic Requirements:
- Tenacity: 3 – 5-gram denier
- Elongation at break: 10 – 35%
- Recovery from elongation: 100% at strains up to 5%
- Modulus of elasticity: 30 – 60-gram denier
- Moisture absorbency: 2 – 5%
- Zero strength temperature (excessive creep and softening point):
above 215°C - High abrasion resistance (varies with type fabric structure)
- Dye-able
- Low flammability
- Insoluble with low swelling in water, in moderately strong acids
and bases and conventional organic solvents at room temperature
to 100°c - Ease of care
Industrial Requirements
Tenacity: 7 – 8 grad denier
Elongation at break: 8 – 15%
Modulus of elasticity: 80 grad denier or more conditioned, 50 grad denier wet
Zero strength temperature: 250° C or above
Basic Textile Fiber Properties
There are several primary properties necessary for a polymeric material to make an adequate fiber. Certain other fiber properties increase its value and desirability in its intended end-use but are not necessary properties essential to make a fiber. Such secondary properties include moisture absorption characteristics, fiber resiliency, abrasion resistance, density, luster, chemical resistance, thermal characteristics, and flammability.
Some Primary Properties of Textile Fibers are:
Fiber length to width ratio,
Fiber uniformity,
Fiber strength and flexibility,
Fiber extensibility and elasticity, and
Fiber cohesiveness.
How heat affects Textile Fiber’s properties
Heat helps the fiber /fabric to gain certain special qualities at certain times and are also harmful at other times. But under special guidance, heat helps fiber acquire the following characteristics
Softening, melting, or decomposition temperatures
The tendency of the fiber and fabric to shrink when heat-relaxed, or stretch when heated and under tension
The ability of the fabric to heat set
The ability of the fabric to function properly at elevated temperatures at one time or repeated use
The ability of the fabric to function properly at room temperature (or some other lower temperature) after
exposure at high temperature for a given period of time
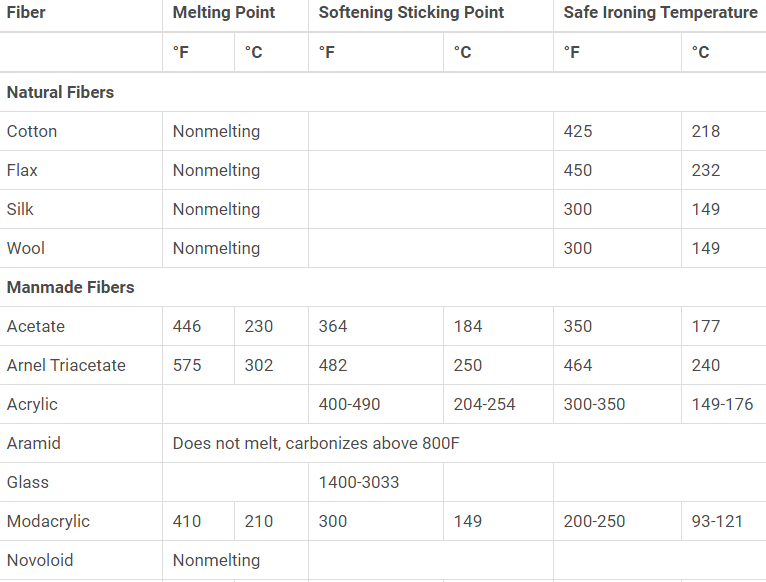
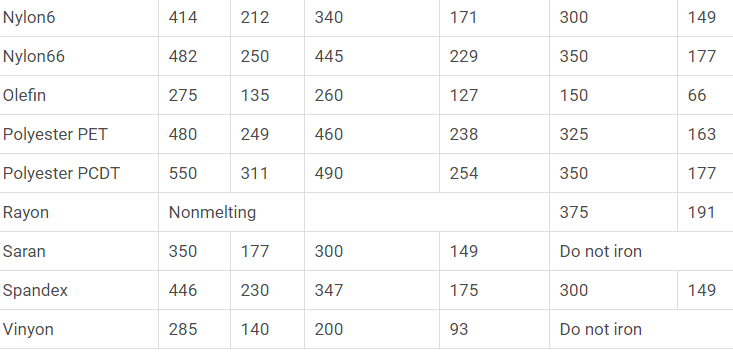
Thermal Properties of Common Fibers:
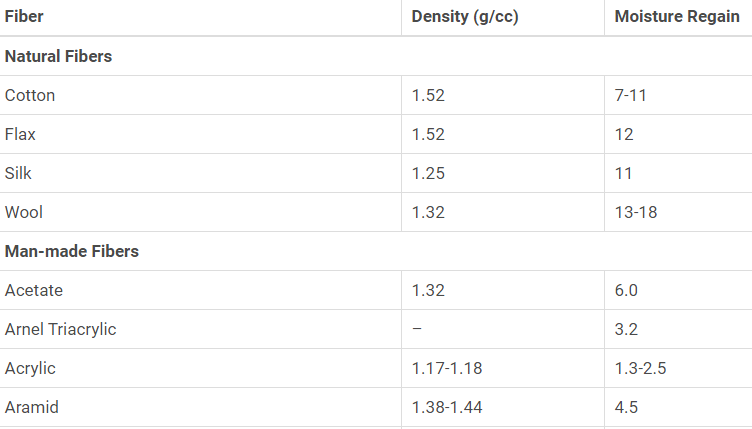
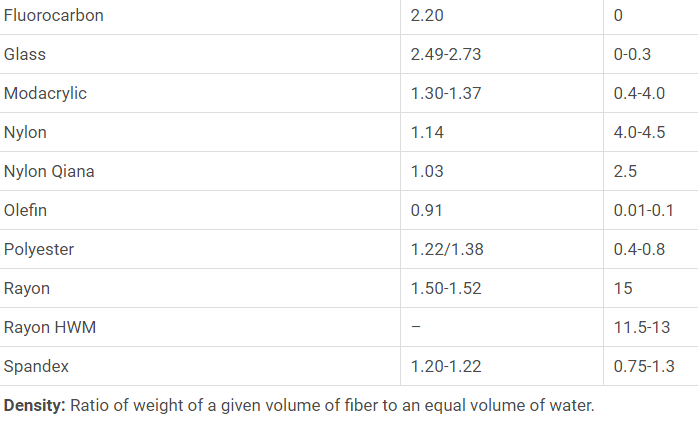
Density and Moisture Regain of Fibers:
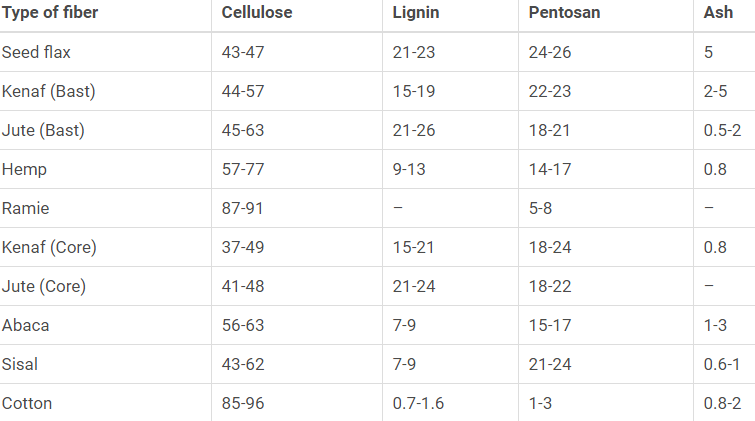
The chemical composition of some common fibers:
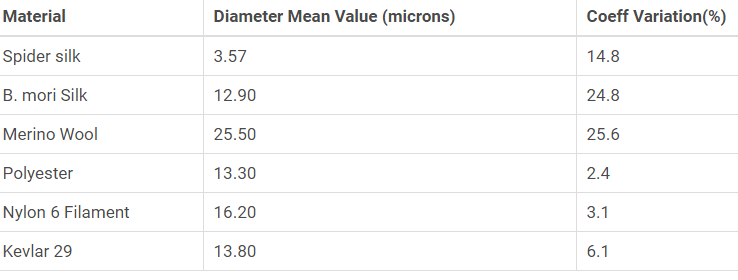
The diameter of Natural and Melt blown Fibers:
Effects of Acids on Common Fibers – Comparison:

Effects of Alkalies on Common Fibers – Comparison:

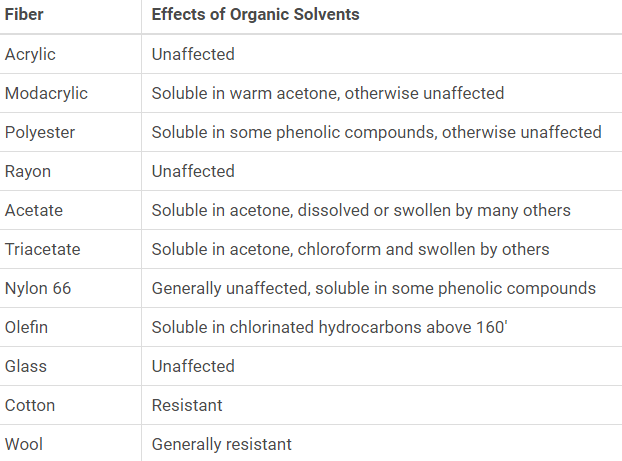
Effects of Organic Solvents on Common Fibers – Comparison: